Introduction
SSL inspection (also known as TLS decryption or HTTPS interception) is a critical feature for Cyfin users, allowing deep analysis of encrypted employee web traffic to identify security threats, enforce policies, and generate comprehensive reports. Without proper SSL inspection, a significant portion of web activity remains hidden, creating blind spots that expose organizations to malware, data exfiltration, and compliance risks. However, enabling SSL inspection isn’t always straightforward. Issues like outdated certificates or enabled QUIC can disrupt functionality, leading to incomplete monitoring and undetected threats.
This knowledge base article outlines common pitfalls when setting up or maintaining SSL inspection, based on industry best practices and known challenges. It provides guidance to help Cyfin customers configure their environments effectively, whether they’re new to SSL inspection or troubleshooting existing setups. By addressing these issues, you can ensure Cyfin delivers full visibility into web traffic while minimizing disruptions.
Why SSL Inspection Matters for Cyfin
Cyfin relies on decrypting SSL/TLS traffic to perform in-depth analysis, such as detecting malicious content, tracking user behavior, and generating accurate reports. Encrypted traffic now accounts for over 90% of web activity, making inspection essential for security. Without it, threats hidden in HTTPS streams— like command-and-control communications or phishing—go unnoticed, increasing the risk of breaches. Proper setup ensures Cyfin can inspect this traffic without compromising network performance or user experience.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Below are key issues that can hinder SSL inspection, along with symptoms, resolutions, and the security risks if left unaddressed. These are drawn from common network security challenges and apply to setups involving firewalls, proxies, or integrated tools like CyBlock (Wavecrest’s companion product for filtering).
1. Outdated or Incorrect Certificates
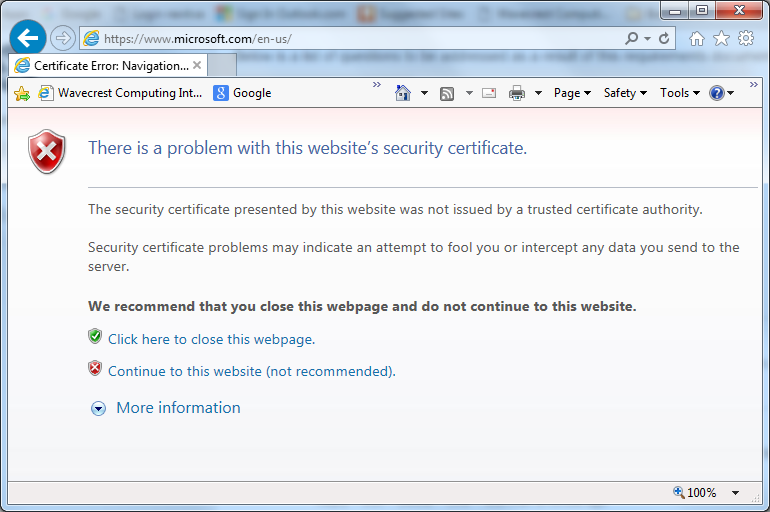
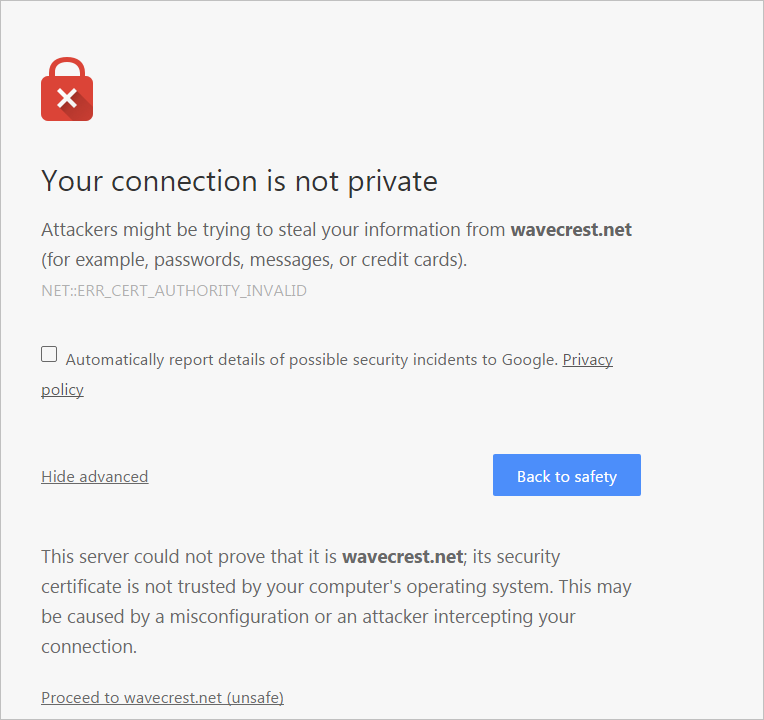
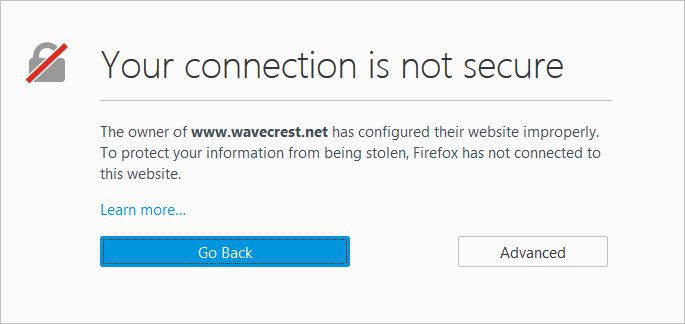
Description: SSL inspection requires generating and using intermediate certificates signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Using expired, revoked, or mismatched certificates (e.g., those with SHA1 algorithms or improper chaining) can cause failures.
Symptoms: Connection errors, browser warnings (e.g., “NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID”), or incomplete decryption, leading to bypassed inspection.
How to Avoid:
- Always use the latest certificates from a reputable CA. Rotate them regularly (e.g., automate short-lived cert issuance).
- Ensure proper PKI implementation: Verify certificate chaining, use correct Subject Alternative Names (SAN), and avoid deprecated algorithms like SHA1.
- For Cyfin integrations, check Wavecrest documentation for certificate generation tools in CyBlock or compatible proxies.
Security Risks if Ignored: Partial or failed decryption leaves encrypted threats undetected, allowing malware or data leaks to bypass Cyfin’s analysis.
2. QUIC Protocol Enabled
Description: QUIC (used in HTTP/3) is a UDP-based protocol with proprietary encryption that most inspection tools, including firewalls, cannot decrypt. It bypasses traditional SSL inspection over TCP.
Symptoms: Traffic to sites like Google or Facebook evades inspection, showing errors like “ERR_QUIC_PROTOCOL_ERROR” or incomplete Cyfin reports.
How to Avoid:
- Block QUIC by denying UDP ports 80 and 443 in your firewall rules, forcing fallback to TCP/TLS.
- Disable QUIC in browsers (e.g., via Chrome flags: chrome://flags/#enable-quic).
- In Cyfin setups, ensure your proxy or firewall (e.g., integrated with CyBlock) has QUIC blocking enabled.
Security Risks if Ignored: QUIC traffic remains uninspected, hiding potential threats and reducing Cyfin’s effectiveness in monitoring employee activity.
3. Lack of CA Certificate Trust on Client Devices
Description: Client devices must trust the inspection device’s root CA certificate for seamless decryption. Without this, browsers and apps reject the intercepted certificates.
Symptoms: Persistent certificate warnings, blocked sites, or apps failing to connect (e.g., in managed environments).
How to Avoid:
- Deploy the CA certificate to all devices via Group Policy (Windows), MDM tools (mobile), or browser trust stores.
- Test on a small group first to ensure compatibility.
- For Cyfin, use Wavecrest’s guides to import certs into CyBlock or your proxy setup.
Security Risks if Ignored: Users may disable inspection to avoid warnings, creating unmonitored traffic and exposing the network to risks Cyfin is designed to detect.
4. Performance Degradation
Description: Decrypting and re-encrypting traffic adds computational load, leading to latency, reduced throughput, and overburdened devices.
Symptoms: Slow network speeds, high CPU usage on firewalls/proxies, or dropped connections during peak times.
How to Avoid:
- Use dedicated hardware or proxy-based solutions like CyBlock, which offload inspection from firewalls.
- Limit inspection to high-risk traffic (e.g., exempt banking sites).
- Distribute load across multiple devices and monitor performance metrics.
Security Risks if Ignored: Overloaded systems may fail to inspect all traffic, allowing threats to slip through undetected by Cyfin.
5. Incompatible Applications or Websites
Description: Some apps/sites use certificate pinning, non-standard protocols, unsupported ciphers, or client certificate authentication, causing inspection to fail.
Symptoms: Specific sites (e.g., with HSTS or pinning) show errors, or apps like banking software refuse connections.
How to Avoid:
- Create bypass rules for known incompatible sites/apps.
- Update inspection devices to support modern ciphers and TLS versions (e.g., TLS 1.3).
- Test thoroughly in a staging environment before rollout.
Security Risks if Ignored: Bypassed traffic remains unmonitored, potentially harboring malware or policy violations invisible to Cyfin.
6. Emerging Technologies and Protocol Changes
Description: New features like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) or Encrypted Client Hello (ECH) obscure traffic metadata, reducing inspection effectiveness.
Symptoms: Incomplete visibility into traffic origins or content, leading to gaps in Cyfin reports.
How to Avoid:
- Block or redirect DoH requests to internal resolvers.
- Stay updated with firmware/patches for your inspection tools.
- Integrate advanced proxies like CyBlock for better handling of evolving encryption.
Security Risks if Ignored: Evolving threats exploit these blind spots, evading Cyfin’s detection and increasing breach likelihood.
7. Privacy, Legal, and Configuration Issues
Description: Improper setup can expose sensitive data, violate privacy laws, or weaken security (e.g., using outdated TLS versions).
Symptoms: User complaints about privacy, legal challenges, or increased vulnerability to attacks.
How to Avoid:
- Exempt sensitive categories (e.g., healthcare) and disclose policies to employees.
- Consult legal experts for compliance.
- Use secure configurations: Enforce strong ciphers and full server validation.
Security Risks if Ignored: Beyond legal fines, misconfigurations can introduce new vulnerabilities, undermining Cyfin’s protective role.
Best Practices for Cyfin Users
- Start Small: Enable inspection for a pilot group to identify issues early.
- Monitor and Update: Regularly review logs, patch systems, and use tools like CyBlock for enhanced filtering.
- Integrate with Wavecrest Tools: Combine Cyfin with CyBlock for proxy-based inspection to avoid firewall overload.
- Educate Users: Explain the benefits to build trust and reduce resistance.
- Test Thoroughly: Simulate traffic to verify setup before full deployment.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, Cyfin customers can achieve robust SSL inspection, maximizing security and visibility. If issues persist, contact Wavecrest support for tailored assistance.